Summary
This article is dedicated to shedding light on boolean recruiting–detailing its mechanics, benefits, and implementation to enhance your candidate sourcing endeavours.
Learn More About Ringover for StaffingWhat is Boolean in recruiting?
Boolean in recruiting is a method of using specific words and symbols, called boolean operators, to refine your search queries on various databases, such as Google, LinkedIn, job boards, or your own ATS or CRM. It was invented by George Boole, an English mathematician and author of The Mathematical Analysis of Logic (1847) and it has significantly influenced the evolution of the search-engine giant, Google.
By using boolean operators, you can include, exclude, or combine certain keywords or phrases to narrow down your search results and find the most relevant candidates for your recruiting outreach. Boolean in recruiting can save you time, money, and effort by allowing you to access a large pool of qualified candidates with minimal effort.
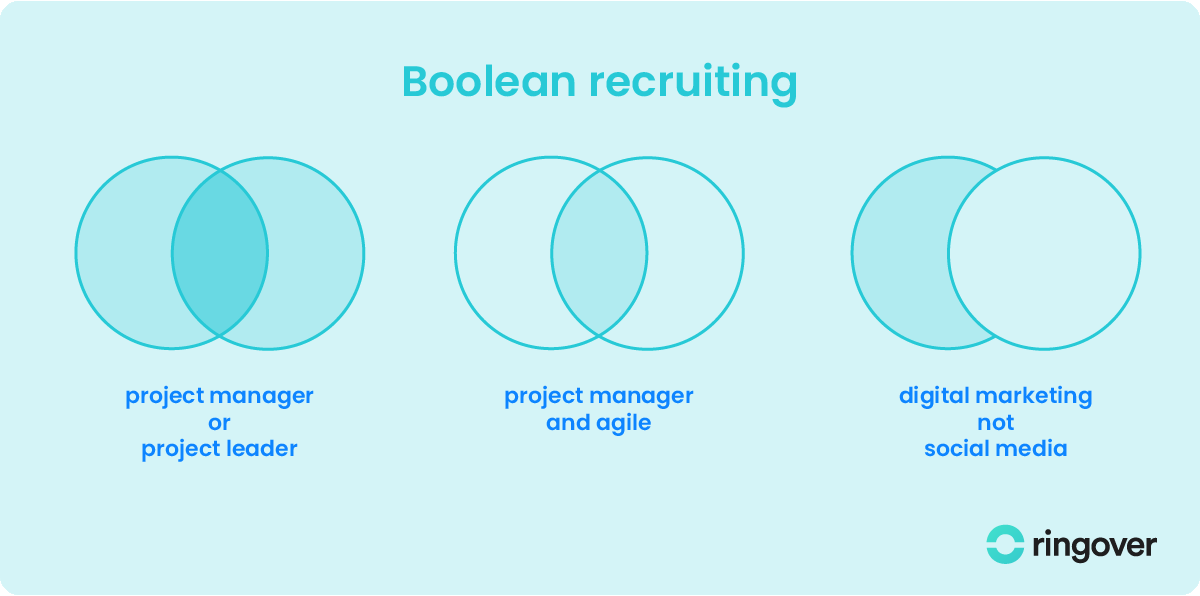
There are three basic boolean operators that you should know: AND, OR, and NOT. There are also some advanced boolean operators, such as NEAR, (), and "".
Once you've mastered these search techniques, you'll be better positioned to find the perfect candidates for your clients and reach out to them using VoIP software. VoIP phones provide omnichannel contact centre software so you can reach candidates (and clients!) in the manner they prefer. After the hard work you've put in finding the right candidate, a cloud telephony tool will support you in candidate relationship management. No more candidates slipping through your fingers!
Table: 5 Boolean Search Examples
Now that you understand what boolean in the recruitment process means and the way to employ basic boolean operators, let's delve into some practical examples. These will illustrate how boolean search strings can be effectively used to pinpoint candidates suitable for various roles and scenarios. Presented below is a table containing five boolean search examples, each accompanied by explanations and the outcomes of the searches.
| Boolean Search String | Explanation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1. "graphic design" AND "social media" | This search signifies the quest for a candidate with expertise in both graphic design and social media. Using quotation marks ensures that the search matches the exact phrases. | Candidates possessing expertise in both "graphic design" and "social media" in their profiles, resumes, or portfolios will be surfaced. |
| 2. art OR design | This search highlights the lookout for a candidate skilled in either art or design. The OR operator widens the search scope to include profiles containing either term. | Profiles featuring either art or design skills in their resumes, portfolios, or personal profiles will be identified. |
| 3. ("news reporter" AND resume) -examples | Here, the search is tailored for a candidate who is a news reporter with an online resume. The minus sign is used to exclude any results containing the word 'examples' to refine the search further. | News reporters with their resumes available online will be found, excluding any sample resumes or news reports. |
| 4. (coding OR programming) AND "UX design" | This search is geared towards finding a candidate with either coding or programming abilities, in addition to UX design skills. Parentheses are used to group terms connected by OR, while AND is utilised to link them with the term "UX design." | Candidates showcasing either coding or programming capabilities along with UX design skills in their profiles, resumes, or portfolios will be discovered. |
| 5. (resume OR CV) AND "search engine optimization" | This search aims at locating a candidate with either a resume or a CV online who has experience in search engine optimization. The inclusion of both terms by OR, combined with AND for the phrase "search engine optimization", broadens the search. | Individuals with a resume or a CV online showcasing experience in search engine optimization in their profiles, resumes, or portfolios will be unearthed. |
These instances demonstrate the versatility of boolean search strings in effective recruitment. Feel free to adapt and refine these searches to better suit your requirements and preferences.
Moreover, mastering advanced boolean operators, such as NEAR, (), and "", can lead to the creation of even more targeted and precise searches, supporting the successful execution of your recruitment strategy. The specifics of these operators will be discussed in upcoming sections.
List: Boolean Operators
We've discussed the foundations of using boolean logic in recruiting, emphasising the significance of AND, OR, and NOT operators. This segment will broaden our exploration, presenting a detailed array of boolean operators for crafting intricate and precise search algorithms. We'll delve into the functionality of each operator, supplemented by practical examples to enhance your search queries.
Explore the array of boolean operators available for your search queries:
- AND: Fetches results containing every keyword linked by it. For instance, "java AND python" filters results to only those including both "java" and "python". Utilise this operator to refine your search, pinpointing candidates with diverse skills or qualifications.
- OR: Yields results that possess any or all of the linked keywords. "java OR python", as an example, would bring up entries with "java", "python", or both. This operator broadens your search scope, identifying candidates with varied skills or qualifications.
- NOT: Generates results that include the initial keyword while excluding the second. A search like "java NOT python" will show entries with "java" but without "python". Employ this operator to filter out irrelevant or undesirable results from your search.
- NEAR: Brings back results where the connected keywords are within a specified proximity to each other. "java NEAR python", for instance, finds entries where "java" and "python" appear closely within the text, aiding in locating candidates with related skills or qualifications.
- (): Enables keyword grouping and precedence in search execution. "(java OR python) AND (developer OR engineer)" would retrieve entries with either "java" or "python", plus either "developer" or "engineer". This operator allows for the aggregation of multiple operators to construct complex search queries.
- "": Returns results containing the precise phrase enclosed within. Searching for ""java developer"" targets entries with the exact phrase "java usurpdeveloper", pinpointing candidates with specific titles or roles.
- *: Retrieves variations of a keyword succeeded by it. For example, "develop*" will return entries containing words starting with "develop", such as "developer", "development", or "developing", useful for finding candidates with similar skills or qualifications.
Creating integrations between your ATS and communications solution ensures a seamless transition from searching for candidates to making contact with them.
List: Boolean Modifiers
Boolean operators are invaluable in refining search queries, but to fine-tune these searches even further, boolean modifiers come into play. These modifiers are specific words and symbols that alter the meaning or interpretation of attached keywords, helping you locate more focused, relevant, or comprehensive search results.
The following boolean modifiers can enhance your search queries:
- Quotation marks "": Encapsulating a phrase within quotation marks will yield results containing that exact phrase. For instance, searching for "java developer" will bring up results with the precise term "java developer". This is particularly useful for pinpointing candidates with specific job titles or roles.
- Asterisk *:. An asterisk following a keyword fetches variations of that word. Searching for develop* will return entries including "developer", "development", "developing", and any other word starting with "develop". This modifier is ideal for discovering candidates with related skills or qualifications.
- Parentheses (): These are used to group keywords together and prioritise the search terms' order. Searching for (java OR python) AND (developer OR engineer) filters results to include either "java" or "python" in conjunction with either "developer" or "engineer". Employing parentheses allows for the combination of various operators to construct intricate search strings.
How to Use Boolean Search on Google
Despite Google's vast resources, finding the perfect results can sometimes be challenging due to the sheer volume of available information. This where mastering the art of boolean search on Google becomes invaluable.
By incorporating boolean logic into your Google searches, you can craft precise, relevant, and exhaustive search strings that yield the most suitable web pages for your requirements.
Engaging with boolean search is straightforward: input your search criteria into Google's search box, incorporating the desired boolean operators and modifiers. For example, to discover pages that contain the exact phrase "boolean recruiting" alongside the word "examples", your query would be: "boolean recruiting" AND examples. This command fetches results that include both the specified phrase and word.
To leverage boolean search on Google effectively, here are essential tips and practices:
- Google generally disregards punctuation not associated with a search operator or modifier, such as the comma in "java, python".
- Avoid adding spaces between an operator or modifier and your search term, e.g., use "site:kinsta.com" rather than "site: kinsta.com".
- Remember, boolean operators are case sensitive. Opt for "AND", "OR", and "NOT" over their lowercase counterparts.
- Enclose exact phrases in quotation marks to narrow your search, like "java developer" instead of java developer.
- Utilise parentheses to group keywords and direct the search sequence, e.g., "(java OR python) AND (developer OR engineer)".
- Apply the asterisk as a wildcard to search for keyword variations, thus "develop*" covers developer, development, or developing.
- Exclude keywords by prefixing them with a minus sign, for instance, "java -python" rather than "java NOT python".
- The pipe symbol "|" functions as an "OR" operator, use "java | python" to search for either term.
- To search within a specific site, use the "site:" operator, as in "site:kinsta.com".
- For finding particular file types, employ the "filetype:" operator, like "filetype:pdf" for PDF documents exclusively.
How to Use Boolean Search on LinkedIn
LinkedIn, with its 800 million members, millions of job postings, company pages, and groups, is a vital tool for recruiters searching for candidates across various industries, locations, and backgrounds. Finding the right candidates amidst the vast user base and intense competition, however, can be challenging.
Enter the power of Boolean search on LinkedIn.
Boolean search enhances your LinkedIn search queries by employing specific operators and modifiers, refining your social recruiting. By crafting detailed, targeted, and comprehensive search strings, Boolean search on LinkedIn significantly increases the probability of discovering candidates who precisely match your criteria.
To harness Boolean search on LinkedIn, simply input your desired query into LinkedIn's search box, incorporating the Boolean operators and modifiers you need. Suppose you're looking for candidates with a "java developer" title and experience in "python". In that case, the query "java developer" AND python will yield profiles featuring both the exact phrase and the keyword.
However, when utilising Boolean search on LinkedIn, remember a few key points to maximise its effectiveness:
- LinkedIn recognizes the Boolean operators: AND, OR, NOT, "", and (). It does not acknowledge NEAR or * operators, nor does it accept - or | as substitutes for NOT or OR. Operators should be in uppercase.
- There's a limitation of 10 keywords per search on LinkedIn. Exceeding this count means only the first 10 are considered, but you can group keywords with parentheses to make them count as one.
- LinkedIn allows different search fields, such as keywords, title, location, industry, company, school, etc. Operators and modifiers can be used within these fields or across them, catering to more refined searches.
- Varying search filters are available for different search needs, including filters by connections, current or past companies, current or past schools, years of experience, and more, helping narrow down to the most fitting candidates.
- Different account types offer different search capabilities; basic accounts have access to elementary searching and filtering, whereas premium accounts like Recruiter or Sales Navigator provide advanced searching, filtering, and the ability to save searches and receive alerts for new matching candidates.

Boolean Recruiting Best Practices
Boolean recruiting leverages specific search logic to pinpoint top candidates, going beyond mere familiarity with boolean operators and modifiers. To harness the full power of boolean recruiting, adhering to best practices is key. This guide highlights essential strategies for a more effective and efficient boolean search process.
- Master the basics: Grasping the foundational logic of boolean searches, along with how each operator and modifier operates, is essential. Familiarise yourself with the syntax and regulations of each platform used in your boolean searches, such as Google, LinkedIn, or ATS for recruiting like Bullhorn, Vincere, or Zoho Recruit. Utilise online tutorials and cheat sheets to bolster your understanding and proficiency in boolean logic.
- Test and refine your search strings: Crafting effective boolean search strings usually requires some experimentation. It's advisable to test your search parameters before deploying them to ensure they yield valuable results. Continuously adjust your search strings by tweaking keywords or operators to hone in on the best candidate matches.
- Combine operators and platforms: Boolean recruiting does not confine you to single operators or platforms. Employ a mix of operators and modifiers for more complex and targeted searches, and explore various platforms for wider candidate reach, such as Google, LinkedIn, or job boards. Leverage specific search functions like 'site:' or 'filetype:' to drill down into particular websites or document types.
- Select specific and relevant keywords: The success of your boolean search heavily depends on the keywords chosen. Opt for precise, role- and industry-specific keywords over generic ones to avoid overwhelming or scant results. Tools like Google Trends or Keyword Tool can assist in identifying high-impact keywords for your searches.
- Practise your search skill: Mastering boolean recruiting demands continual learning and application. Challenge yourself to adopt new search strategies and engage with online resources or tools like Boolean Builder or SeekOut. Participating in forums such as SourceCon or the Boolean Strings Network can offer valuable insights from peers and experts alike.
- Review and document your search strings: Boolean searches are iterative, necessitating regular examination and documentation for ongoing refinement. Keeping track of the outcomes of your searches, including staffing analytics like the number of candidates sourced or hired, is integral. Tools such as Recruitee or Zoho Recruit can streamline the management and evaluation of your boolean search efforts.
Conclusion
Mastering boolean recruiting is an evolving journey necessitating ongoing practice and refinement. It's crucial to experiment with your search strings, select keywords judiciously, integrate various operators and platforms, systematically record your search strategies, and monitor the results and effectiveness of your efforts.
With boolean search techniques, you'll be able to get the most out of your recruiting tools so you can find the best candidates for your clients.
Boolean Recruiting FAQ
What are the 3 Boolean searches?
The core of boolean recruitment lies in three fundamental operators: AND, OR, and NOT. These operators help refine your search by including, excluding, or merging specific keywords or phrases, thereby narrowing or expanding your search results.
For instance, searching for "java AND python" filters for results containing both terms, "java OR...python" fetches results with either term, and "java NOT python" isolates results featuring "java" but not "python".
What is an example of a Boolean?
Boolean logic works with true or false values to conclude statements or conditions. For example, given A is true and B is false, then A AND B results in false, A OR B equals true, and NOT A turns out false. In boolean recruiting, a boolean entails a search string that leverages boolean operators and modifiers to yield more targeted, relevant, and comprehensive search outcomes. A practical boolean search could be "java developer" AND (python OR... or ruby) AND NOT "junior", ensuring results include "java developer" alongside "python" or "ruby" but exclude "junior".
What is an example of a Boolean string search used in recruiting?
Boolean string searches in recruitment utilise boolean operators and modifiers to scout for specific candidate profiles or needs. For instance, searching for an agile-experienced project manager adept in digital marketing might look like: ("project manager" OR "project leader") AND agile AND ("digital marketing" OR SEO OR SEM OR "social media"), pinpointing profiles with "project manager" or "project leader," "agile," and any of the listed digital marketing skills.




